With a “learn how” post like this one, as a reader you don’t want a long intro. You just want to get to the point. So simply put, this post will explain how WebRTC and WebSockets can work together to build a chat-based application.
How Can Your Application Achieve Real Time Communication between Browsers?
WebRTC gives the web browser the capability to connect users to share video, audio and data content directly, this is known as peer-to-peer communication; this is fantastic but in real world applications, we should do a couple of extra things to have the whole flow fully operational.
It’s like if we want to send a letter, we are free to send it to anybody but in addition to the receiver name, we must know its location to be able to deliver the message (among other things). The same occurs with WebRTC, it opens a window to share media content with other peers, but before that we need to exchange some initial information with the counterpart following a specific process.
In the WebRTC ecosystem the process to exchange information with other peers to establish communication is known as “Signaling” and we can list some common actions to describe that process:
- Login: A user accesses and identifies himself in the web application
- Call: A user wants to establish communication with another user
- Answer: A user answers another user’s call
- Hangout: A user desires to finish the communication
What Do You Need to Implement Signaling in Your Application?
The Signaling process is out of the scope of WebRTC (at least at the beginning), so we need a complementary tool to be in charge of it, here is where Websockets come to the rescue.
There are other options to manage the signaling process, but implementing a WebSocket server is one of the approaches that offer more advantages:
- Support across all browsers
- It’s an old acquaintance for web developers
- Easy to implement
- The client/server communication is reliable
- Additional business logic can be added before establishing the communication
- Can be an option to implementing a fallback strategy
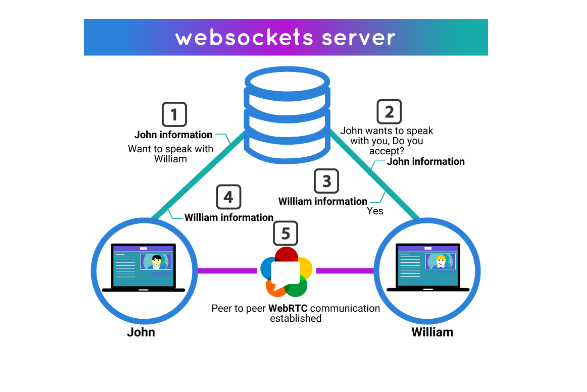
To make it easier to explain how WebSockets works together with WebRTC, we can use the following diagram:
- John calls William. His information is sent along with the request
- The WebSocket server asks William if he wants to answer John’s call. William receives John’s information
- William accepts and answers John’s call. His information is sent along with the response
- John receives William’s information
- WebRTC establish the peer to peer communication
In a nutshell, in order to establish a real time communication, John and William must exchange information that WebRTC needs to connect peers.
The WebSockets server is in the middle for this important task. Once each peer has the information required to sharing multimedia data, the direct communication can now start.
In this post we have taken a look (in high level) at how WebSockets and WebRTC can work together to build real world applications.
This is just the beginning.
If you want to know how to setup your own WebSocket server or see a live demo of these cool technologies, stay tuned for future posts.
Contact us to build or improve your WebRTC app!
Do you need more information on how to have WebRTC work in your web application? Do you need help implementing chat-based features in your next project? We have an experienced team ready & happy to help you out.